field_automation 机制
定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
src / ch2 / section2 .3 / 2.3.7 / my_transaction . sv
class my_transaction extends uvm_sequence_item ;
rand bit [ 47 : 0 ] dmac ;
rand bit [ 47 : 0 ] smac ;
rand bit [ 15 : 0 ] ether_type ;
rand byte pload [];
rand bit [ 31 : 0 ] crc ;
…
`uvm_object_utils_begin ( my_transaction )
`uvm_field_int ( dmac , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( smac , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( ether_type , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_array_int ( pload , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( crc , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_object_utils_end
…
endclass
上述代码中是先放入dmac, 再依次放入smac、 ether_type、 pload、 crc 是按field 的先后顺序来排的uvm_object_utils_begin 和 uvm_object_utils_end 来实现my_transaction的factory注册,
使用:
当使用上述宏注册之后, 可以直接调用copy、 compare、 print等函数, 而无需自己定义。 这极大地简化了验证平台的搭建, 提
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
文件: src / ch2 / section2 .3 / 2.3.7 / my_model . sv
task my_model :: main_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
my_transaction tr ;
my_transaction new_tr ;
super . main_phase ( phase );
while ( 1 ) begin
port . get ( tr ); // 从 FIFO 获得 tr
new_tr = new ( "new_tr" );
new_tr . copy ( tr ); // 复制 tr 中的数据 uvm_object_utils_begin和uvm_object_utils_end 包起来的数据
`uvm_info ( "my_model" , "get one transaction, copy and print it:" , UVM_LOW )
new_tr . print (); // 格式化打印 tr 中 uvm_object_utils_begin和uvm_object_utils_end 包起来的数据
ap . write ( new_tr );
end
endtask
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
文件: src / ch2 / section2 .3 / 2.3.7 / my_scoreboard . sv
…
while ( 1 ) begin
act_port . get ( get_actual );
if ( expect_queue . size () > 0 ) begin
tmp_tran = expect_queue . pop_front ();
result = get_actual . compare ( tmp_tran );
if ( result ) begin
`uvm_info ( "my_scoreboard" , "Compare SUCCESSFULLY" , UVM_LOW );
end
…
上述例子直接调用 compare 来进行比较
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
文件: src / ch2 / section2 .3 / 2.3.7 / my_driver . sv
task my_driver :: drive_one_pkt ( my_transaction tr );
byte unsigned data_q [];
int data_size ;
data_size = tr . pack_bytes ( data_q ) / 8 ;
`uvm_info ( "my_driver" , "begin to drive one pkt" , UVM_LOW );
repeat ( 3 ) @( posedge vif . clk );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < data_size ; i ++ ) begin
@( posedge vif . clk );
vif . valid <= 1 'b1 ;
vif . data <= data_q [ i ];
end
@( posedge vif . clk );
vif . valid <= 1 'b0 ;
`uvm_info ( "my_driver" , "end drive one pkt" , UVM_LOW );
endtask
上述例子调用pack_bytes将tr中所有的字段变成byte流放入data_q中
与uvm_object 相关的宏
uvm_object_utils
它用于把一个直接或间接派生自uvm_object的类注册到factory中
uvm_object_param_utils
它用于把一个直接或间接派生自uvm_object的参数化的类注册到factory中
1
class A #( int WIDTH = 32 ) extends uvm_object ;
参数化的类在代码可重用性中经常用到。 如果允许, 尽可能使用参数化的类, 它可以提高代码的可移植性
uvm_object_utils_begin
这个宏在第2章介绍my_transaction时出现过, 当需要使用field_automation 机制 时, 需要使用此宏。
1
2
`uvm_object_utils_begin ( my_object )
`uvm_object_utils_end
答案是不会出现任何问题, 这样的写法完全正确, 可以尽情使用。
uvm_object_param_utils_begin
uvm_object_param_utils_begin: 与uvm_object_utils_begin宏一样, 只是它适用于参数化的且其中某些成员变量要使用 field_automation机制实现的类
uvm_object_utils_end:
它总是与uvm_object_*_begin成对出现, 作为factory注册的结束标志。
与uvm_component相关的宏
uvm_component_utils:
它用于把一个直接或间接派生自uvm_component的类注册到factory中
uvm_component_param_utils:
它用于把一个直接或间接派生自uvm_component的参数化的类注册到factory中
uvm_component_utils_begin:
这个宏与uvm_object_utils_begin相似, 它用于同时需要使用factory机制和field_automation机制注册对于uvm_component来说最大的意义不在于此, 而在于可以自动地使用config_db来得到某些变量的值。 具体的可以参考3.5.3节的
uvm_component_param_utils_begin:
与uvm_component_utils_begin宏一样, 只是它适用于参数化的, 且其中某些成员变量要使用field_automation机制实现的类。
uvm_component_utils_end:
它总是与uvm_component_*_begin成对出现, 作为factory注册的结束标志。
uvm_component的限制
uvm_component是从uvm_object派生来的。 从理论上来说, uvm_component应该具有uvm_object的所有的行为特征。 但是, 由
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class A extends uvm_object ;
…
endclass
class my_env extends uvm_env ;
virtual function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
A a1 ;
A a2 ;
a1 = new ( "a1" );
a1 . data = 8'h9 ;
$cast ( a2 , a1 . clone ());
endfunction
endclass
上述的clone函数无法用于uvm_component中, 因为一旦使用后, 新clone出来的类, 其parent参数无法指定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class A extends uvm_component ;
…
endclass
class my_env extends uvm_env ;
virtual function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
A a1 ;
A a2 ;
a1 = new ( "a1" , this );
a2 = new ( "a1" , this );
endfunction
endclass
uvm_component 中的 parent 参数
UVM通过uvm_component来实现树形结构。 所有的UVM树的结点本质上都是一个uvm_component。 每个uvm_component都有
1
function new ( string name , uvm_component parent );
一般在使用时, parent通常都是this。 假设A和B均派生自uvm_component, 在A中实例化一个B:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class B extends uvm_component ;
… e
ndclass
class A extends uvm_component ;
B b_inst ;
virtual function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
b_inst = new ( "b_inst" , this );
endfunction
endclass
在b_inst实例化的时候, 把this指针传递给了它, 代表A是b_inst的parent。 为什么要指定这么一个parent呢? 一种常见的观点
1
b_inst = new ( "b_inst" );
虽然默认parent 是 this, 但是这种写法是不对的, 原因比较长, 这里不记录了, 详见 UVM 实战 P163
UVM 树的根
完整的UVM树
1
env = my_env :: type_id :: create ( "env" , this );
但是, 假如不按照上面的写法, 向parent参数传递一个null会如何呢?
1
env = my_env :: type_id :: create ( "env" , null );
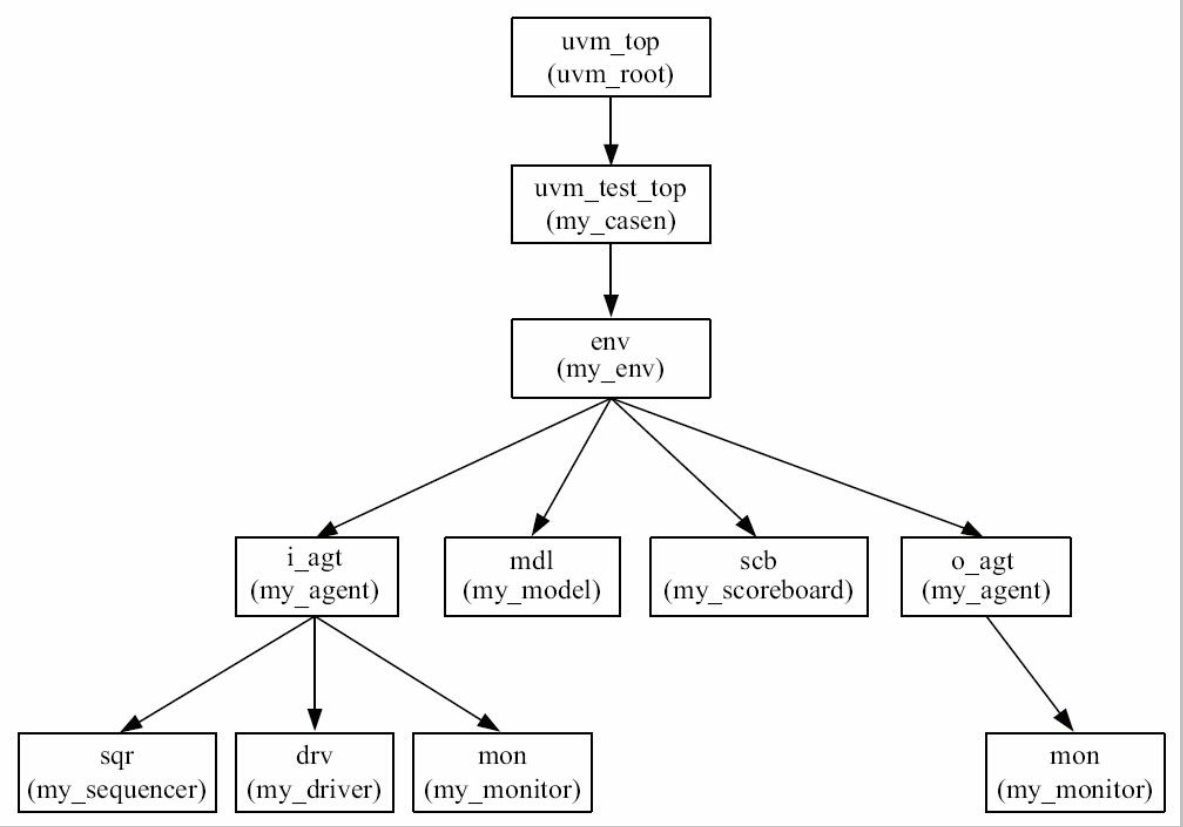
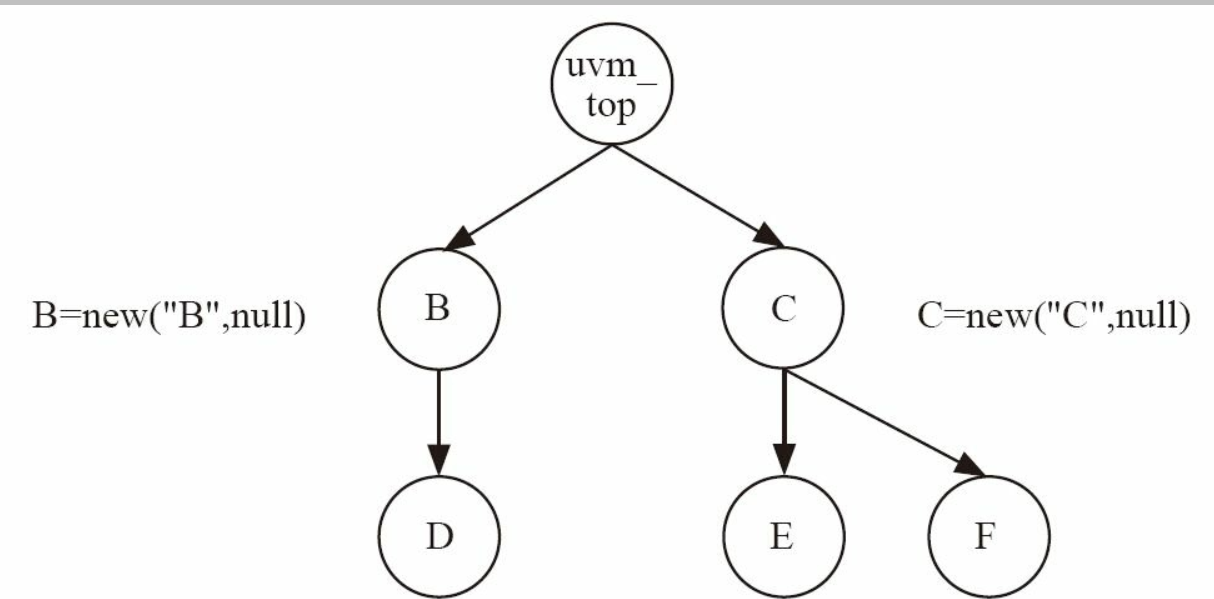
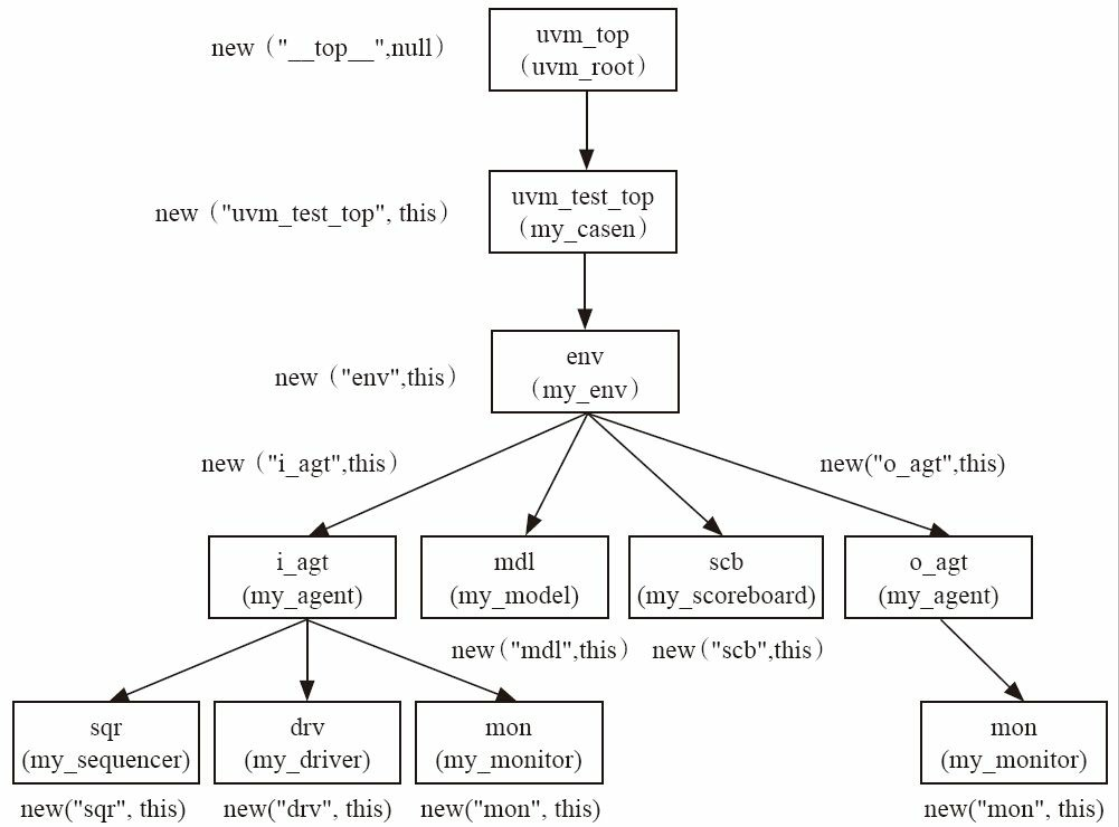
如果一个component在实例化时, 其parent被设置为null, 那么这个component的parent将会被系统设置为系统中唯一的uvm_root 的实例uvm_top, 如下图所示:
可见, uvm_root的存在可以保证整个验证平台中只有一棵树, 所有结点都是uvm_top的子结点。
1
2
uvm_root top ;
top = uvm_root :: get ();
层次结构相关的函数
get_parent
用于得到当前实现的 parent
1
extern virtual function uvm_component get_parent ();
get_child
用于得到当前实现的 child
1
extern function uvm_component get_child ( string name );
get_child需要一个string类型的参数name, 表示此child实例在实例化时指定的名字, 这个名字可以使用 get_children 函数得到
get_children
get_children
原型:
1
extern function void get_children ( ref uvm_component children [ $ ]);
e.g
1
2
3
4
uvm_component array [ $ ];
my_comp . get_children ( array );
foreach ( array [ i ])
do_something ( array [ i ]);
get_first_child和get_next_child
除了一次性得到所有的child外, 还可以使用get_first_child和get_next_child的组合依次得到所有的child:
1
2
extern function int get_first_child ( ref string name );
extern function int get_next_child ( ref string name );
ref 即相当于指针的意思, get_first_child 把获得的值存到 ref 变量里
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
string name ;
uvm_component child ;
if ( comp . get_first_child ( name ))
do begin
child = comp . get_child ( name );
child . print ();
end while ( comp . get_next_child ( name ));
field_automation 机制详解
宏相关
uvm_field 宏的种类
1
2
3
4
5
6
`define uvm_field_int(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_real(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_enum(T,ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_object(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_event(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_string(ARG,FLAG)
上述几个宏分别用于要注册的字段是整数、 实数、 枚举类型、 直接或间接派生自uvm_object的类型、 事件及字符串类型。 这
1
2
3
4
5
typedef enum { TB_TRUE , TB_FALSE } tb_bool_e ;
…
tb_bool_e tb_flag ;
…
`uvm_field_enum ( tb_bool_e , tb_flag , UVM_ALL_ON )
与动态数组有关的uvm_field系列宏
1
2
3
4
`define uvm_field_array_enum(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_array_int(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_array_object(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_array_string(ARG,FLAG)
与静态数组相关的uvm_field系列宏
1
2
3
4
`define uvm_field_sarray_int(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_sarray_enum(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_sarray_object(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_sarray_string(ARG,FLAG)
与队列相关的uvm_field系列宏
1
2
3
4
`define uvm_field_queue_enum(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_queue_int(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_queue_object(ARG,FLAG)
`define uvm_field_queue_string(ARG,FLAG)
与联合数组相关的uvm_field宏
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
`define uvm_field_aa_int_string(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_string_string(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_object_string(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_int(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_int_unsigned(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_integer(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_integer_unsigned(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_byte(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_byte_unsigned(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_shortint(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_shortint_unsigned(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_longint(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_int_longint_unsigned(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_string_int(ARG, FLAG)
`define uvm_field_aa_object_int(ARG, FLAG)
这里一共出现了15种。 联合数组有两大识别标志, 一是索引的类型, 二是存储数据的类型。 在这一系列uvm_field系列宏中,
宏中与if 结合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
`uvm_object_utils_begin ( my_transaction )
`uvm_field_int ( dmac , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( smac , UVM_ALL_ON )
if ( is_vlan ) begin
`uvm_field_int ( vlan_info1 , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( vlan_info2 , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( vlan_info3 , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( vlan_info4 , UVM_ALL_ON )
end
`uvm_field_int ( ether_type , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_array_int ( pload , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( crc , UVM_ALL_ON | UVM_NOPACK )
`uvm_field_int ( is_vlan , UVM_ALL_ON | UVM_NOPACK )
`uvm_object_utils_end
函数相关
copy
1
extern function void copy ( uvm_object rhs );
如果要把某个A实例复制到B实例中, 那么应该使用B.copy( A) 。 在使用此函数前, B实例必须已经使用new函数分配好了内
compare
1
extern function bit compare ( uvm_object rhs , uvm_comparer comparer = null );
如果要比较A与B是否一样, 可以使用A.compare( B) , 也可以使用B.compare( A) 。 当两者一致时, 返回1; 否则为0。
pack_bytes
1
extern function int pack_bytes ( ref byte unsigned bytestream [], input uvm_packer packer = null );
用于将所有的字段打包成byte流
1
2
3
byte unsigned data_q [];
int data_size ;
data_size = tr . pack_bytes ( data_q ) / 8 ;
unpack_bytes
1
extern function int unpack_bytes ( ref byte unsigned bytestream [], input uvm_packer packer = null );
用于将一个byte流逐一恢复到某个类的实例中
pack
1
extern function int pack ( ref bit bitstream [], input uvm_packer packer = null );
用于将所有的字段打包成bit流, pack函数的使用与pack_bytes类似。
unpack
1
extern function int unpack ( ref bit bitstream [], input uvm_packer packer = null );
用于将一个bit流逐一恢复到某个类的实例中, unpack的使用与unpack_bytes类似
pack_ints
1
extern function int pack_ints ( ref int unsigned intstream [], input uvm_packer packer = null );
用于将所有的字段打包成int( 4个byte, 或者dword) 流
unpack_ints
1
extern function int unpack_ints ( ref int unsigned intstream [], input uvm_packer packer = null );
用于将一个int流逐一恢复到某个类的实例中
print
用于打印所有的字段
clone
1
extern virtual function uvm_object clone ();
标志位的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
//A=ABSTRACT Y=PHYSICAL
//F=REFERENCE, S=SHALLOW, D=DEEP
//K=PACK, R=RECORD, P=PRINT, M=COMPARE, C=COPY
//--------------------------- AYFSD K R P M C
parameter UVM_ALL_ON = 'b000000101010101 ;
parameter UVM_COPY = ( 1 << 0 );
parameter UVM_NOCOPY = ( 1 << 1 );
parameter UVM_COMPARE = ( 1 << 2 );
parameter UVM_NOCOMPARE = ( 1 << 3 );
parameter UVM_PRINT = ( 1 << 4 );
parameter UVM_NOPRINT = ( 1 << 5 );
parameter UVM_RECORD = ( 1 << 6 );
parameter UVM_NORECORD = ( 1 << 7 );
parameter UVM_PACK = ( 1 << 8 );
parameter UVM_NOPACK = ( 1 << 9 );
在这个17bit的数字中, bit0表示copy, bit1表示no_copy, bit2表示compare, bit3表示no_compare, bit4表示print, bit5表示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
class my_transaction extends uvm_sequence_item ;
rand bit [ 47 : 0 ] dmac ;
rand bit [ 47 : 0 ] smac ;
rand bit [ 15 : 0 ] ether_type ;
rand byte pload [];
rand bit [ 31 : 0 ] crc ;
rand bit crc_err ;
…
function void post_randomize ();
if ( crc_err )
; //do nothing
else
crc = calc_crc ;
endfunction
…
endclass
这样, 在post_randomize中计算CRC前先检查一下crc_err字段, 如果为1, 那么直接使用随机值, 否则使用真实的CRC
1
`uvm_do_with ( tr , { tr . crc_err == 1 ;})
只是, 对于多出来的这个字段, 是不是也应该用uvm_field_int宏来注册呢? 如果不使用宏注册的话, 那么当调用print函数时,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
`uvm_object_utils_begin ( my_transaction )
`uvm_field_int ( dmac , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( smac , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( ether_type , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_array_int ( pload , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( crc , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_field_int ( crc_err , UVM_ALL_ON | UVM_NOPACK )
`uvm_object_utils_end
使用上述语句后, 当执行pack和unpack操作时, UVM就不会考虑这个字段了
UVM 打印信息的控制
打印冗余度阈值
冗余度阈值定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
typedef enum
{
UVM_NONE = 0 ,
UVM_LOW = 100 ,
UVM_MEDIUM = 200 ,
UVM_HIGH = 300 ,
UVM_FULL = 400 ,
UVM_DEBUG = 500
} uvm_verbosity ;
默认的冗余度阈值是UVM_MEDIUM, 所有低于等于 UVM_MEDIUM( 如UVM_LOW) 的信息都会被打印出来。
get_report_verbosity_level
可以通过 get_report_verbosity_level 函数得到某个component的冗余度阈值 ( 这个值是个整数, 对应UVM_LOW 等 )
1
2
3
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
$display ( "env.i_agt.drv's verbosity level is %0d" , env . i_agt . drv . get_report_verbosity_level ());
endfunction
set_report_verbosity_level
UVM提供set_report_verbosity_level函数来设置某个特定component的默认冗余度阈值。
1
2
3
4
5
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.1 / base_test . sv
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_verbosity_level ( UVM_HIGH );
…
endfunction
由于需要牵扯到层次引用, 所以需要在connect_phase及以后的phase才能调用这个函数。 如果不牵扯到任何层次引用, 如设置
set_report_verbosity_level_hier
递归的设置冗余度函数
1
env . i_agt . set_report_verbosity_level_hier ( UVM_HIGH );
把env.i_agt及其下所有的component的冗余度阈值设置为UVM_HIGH
set_report_id_verbosity
区分不同的ID的冗余度阈值
1
2
`uvm_info ( "ID1" , "ID1 INFO" , UVM_HIGH )
`uvm_info ( "ID2" , "ID2 INFO" , UVM_HIGH )
使用下面语句后 ID1 INFO 会显示 但 ID2 INFO 不会显示
1
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_verbosity ( "ID1" , UVM_HIGH );
set_report_id_verbosity_hier
递归的实现 set_report_id_verbosity 相同的功能
1
env . i_agt . set_report_id_verbosity_hier ( "ID1" , UVM_HIGH );
在命令行中设置冗余度阀值
1
2
3
4
< sim command > + UVM_VERBOSITY = UVM_HIGH
或者:
< sim command > + UVM_VERBOSITY = HIGH
上面两个命令行参数是等价的, 即可以把冗余度级别的前缀“ UVM_ ”省略。
上述的命令行参数会把整个验证平台的冗余度阈值设置为UVM_HIGH。 它几乎相当于是在base_test中调用
1
set_report_verbosity_level_hier ( UVM_HIGH )
把base_test及以下所有component的冗余度级别设置为UVM_HIGH
重载打印信息的严重性
set_report_severity_override
重载是深入到UVM骨子里的一个特性。 UVM默认有四种信息严重性: UVM_INFO、 UVM_WARNING、 UVM_ERROR、
1
2
3
4
5
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.2 / base_test . sv
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_override ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_ERROR );
//env.i_agt.drv.set_report_severity_id_override(UVM_WARNING, "my_driver", UVM_ERROR);
endfunction
重载前
1
`uvm_warning ( "my_driver" , "this information is warning, but prints as UVM_ERROR" )
重载后
1
`uvm_warning ( "my_driver" , "this information is warning, but prints as UVM_ERROR" )
set_report_severity_id_override
重载严重性可以只针对某个component内的某个特定的ID起作用:
1
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_id_override ( UVM_WARNING , "my_driver" , UVM_ERROR );
只重载 ID 为 my_driver 的 UVM_WARNING 为 UVM_ERROR
命令行重载严重性
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_severity =< comp > , < id > , < current severity > , < new severity >
设置单个ID
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_severity = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,my_driver,UVM_WARNING,UVM_ERROR"
设置所有ID
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_severity = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,_ALL_,UVM_WARNING,UVM_ERROR"
UVM_ERROR 到达一定数量结束仿真
当uvm_fatal出现时, 表示出现了致命错误, 仿真会马上停止。 UVM同样支持UVM_ERROR达到一定数量时结束仿真。 这个功
set_report_max_quit_count
1
2
3
4
5
6
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.3 / base_test . sv
function void base_test :: build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
env = my_env :: type_id :: create ( "env" , this );
set_report_max_quit_count ( 5 );
endfunction
上述代码把退出阈值设置为5。 当出现5个UVM_ERROR时, 会自动退出, 并显示如下的信息:
1
2
3
4
# --- UVM Report Summary ---
#
# Quit count reached!
# Quit count : 5 of 5
在测试用例中的设置方式与base_test中类似。 如果测试用例与base_test中同时设置了, 则以测试用例中的设置为准。 此外, 除
get_max_quit_count
可以用于查询当前的退出阈值。 如果返回值为0则表示无论出现多少个
1
function int get_max_quit_count ();
在命令行中设置退出阀值
1
< sim command > + UVM_MAX_QUIT_COUNT = 6 , NO
其中第一个参数6表示退出阈值, 而第二个参数NO表示此值是不可以被后面的设置语句重载, 其值还可以是YES。
设置计数的目标
默认的是只有 UVM_ERROR 加入计数目标
set_report_severity_action
加入计数
1
2
3
4
5
6
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.4 / base_test . sv
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
set_report_max_quit_count ( 5 );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT );
…
endfunction
移除计数
1
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY );
set_report_severity_action_hier
递归的实现 set_report_severity_action 相同的功能
加入计数
1
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_action_hier ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT );
移除计数
1
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_action_hier ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY );
set_report_severity_action及set_report_severity_action_hier的第一个参数除了是UVM_WARNING外, 还可以是UVM_INFO
set_report_id_action
对某个特定的ID进行计数
1
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_action ( "my_drv" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT );
上述代码把ID为my_drv的所有信息加入到计数中, 无论是UVM_INFO, 还是UVM_WARNING或者是UVM_ERROR、 UVM_FATAL。
set_report_id_action_hier
递归的实现 set_report_id_action 相同的功能
1
env . i_agt . set_report_id_action_hier ( "my_drv" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT );
set_report_severity_id_action
1
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_id_action ( UVM_WARNING , "my_driver" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT );
同时把 严重性和 id 加入计数
set_report_severity_id_action_hier
递归的实现 set_report_severity_id_action_hier 相同的功能
1
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_id_action_hier ( UVM_WARNING , "my_driver" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT );
命令行中设置计数目标
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_action =< comp > , < id > , < severity > , < action >
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_action = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,my_driver,UVM_NG,UVM_DISPLAY|UVM_COUNT"
若要针对所有的ID设置, 可以使用_ALL_代替ID:
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_action = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,_ALL_,UVM_WARNING,UVM_DISPLAY|UVM_COUNT"
UVM 的断点功能
断点功能需要从仿真器的角度进行设置, 不同仿真器的设置方式不同。 为了消除这些设置方式的不同, UVM支持内建的断点
set_report_severity_action
1
2
3
4
5
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.5 / base_test . sv
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_STOP );
…
endfunction
命令行设置断点
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_action = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,my_driver,UVM_WARNING,UVM_DISPLAY|UVM_STOP"
将输出信息导入文件中
set_report_severity_file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.6 / severity / base_test . sv
UVM_FILE info_log ;
UVM_FILE warning_log ;
UVM_FILE error_log ;
UVM_FILE fatal_log ;
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
info_log = $fopen ( "info.log" , "w" );
warning_log = $fopen ( "warning.log" , "w" );
error_log = $fopen ( "error.log" , "w" );
fatal_log = $fopen ( "fatal.log" , "w" );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_file ( UVM_INFO , info_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_file ( UVM_WARNING , warning_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_file ( UVM_ERROR , error_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_file ( UVM_FATAL , fatal_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_INFO , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_ERROR , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_FATAL , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_EXIT | UVM_LOG );
…
endfunction
上述代码将env.i_agt.drv的UVM_INFO输出到info.log, UVM_WARNING输出到warning.log, UVM_ERROR输出到error.log, UVM_FATAL输出到fatal.log。
set_report_severity_file_hier
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_file_hier ( UVM_INFO , info_log );
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_file_hier ( UVM_WARNING , warning_log );
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_file_hier ( UVM_ERROR , error_log );
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_file_hier ( UVM_FATAL , fatal_log );
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_action_hier ( UVM_INFO , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_action_hier ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_action_hier ( UVM_ERROR , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . set_report_severity_action_hier ( UVM_FATAL , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_EXIT | UVM_LOG );
上述代码将env.i_agt及其下所有结点的输出信息分类输出到不同的日志文件中。
set_report_id_file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.6 / id / base_test . sv
UVM_FILE driver_log ;
UVM_FILE drv_log ;
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
driver_log = $fopen ( "driver.log" , "w" );
drv_log = $fopen ( "drv.log" , "w" );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_file ( "my_driver" , driver_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_file ( "my_drv" , drv_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_action ( "my_driver" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_action ( "my_drv" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
…
endfunction
virtual function void final_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
$fclose ( driver_log );
$fclose ( drv_log );
endfunction
set_report_id_file_hier
递归的实现set_report_id_file 相同的功能
set_report_severity_id_file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.6 / id_severity / base_test . sv
UVM_FILE driver_log ;
UVM_FILE drv_log ;
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
driver_log = $fopen ( "driver.log" , "w" );
drv_log = $fopen ( "drv.log" , "w" );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_id_file ( UVM_WARNING , "my_driver" , driver_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_id_file ( UVM_INFO , "my_drv" , drv_log );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_action ( "my_driver" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_id_action ( "my_drv" , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_LOG );
…
endfunction
以上代码把 UVM_WARNING 和 ID 为 “my_driver” 的打印信息输出到 driver_log
set_report_severity_id_file_hier
递归的实现set_report_severity_id_file 相同的功能
控制打印信息的行为
UVM共定义了如下几种行为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
typedef enum
{
UVM_NO_ACTION = 'b000000 ,
UVM_DISPLAY = 'b000001 ,
UVM_LOG = 'b000010 ,
UVM_COUNT = 'b000100 ,
UVM_EXIT = 'b001000 ,
UVM_CALL_HOOK = 'b010000 ,
UVM_STOP = 'b100000
} uvm_action_type ;
其中:
1
2
3
4
set_severity_action ( UVM_INFO , UVM_DISPLAY );
set_severity_action ( UVM_WARNING , UVM_DISPLAY );
set_severity_action ( UVM_ERROR , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT );
set_severity_action ( UVM_FATAL , UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_EXIT );
用于设置打印行为的函数
set_report_severity_action
set_report_severity_action_hier
set_report_id_action
set_report_id_action_hier
set_report_severity_id_action
set_report_severity_id_action_hier
关闭输出
1
2
3
4
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .4 / 3.4.7 / base_test . sv
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
env . i_agt . drv . set_report_severity_action ( UVM_INFO , UVM_NO_ACTION );
endfunction
无论原本的冗余度是什么, 经过上述设置后, env.i_agt.drv的所有的uvm_info信息都不会输出。
config_db 机制
UVM 中的路径
1
2
3
4
function void my_driver :: build_phase ();
super . build_phase ( phase );
$display ( "%s" , get_full_name ());
endfunction
在component( 如my_driver) 内通过get_full_name( ) 函数可以得到此component的路径
set与get函数的参数
set
如在某个测试用例的build_phase中可以使用如下方式寄信
1
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 100 );
其中第一个和第二个参数联合起来组成目标路径, 与此路径符合的目标才能收信。
第一个参数必须是一个uvm_component实例的指针,
第二个参数是相对此实例的路径。
第三个参数表示一个记号, 用以说明这个值是传给目标中的哪个成员的,
第四个参数是要设置的值
get
在 driver 中的build_phase 使用如下方式收信
1
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: get ( this , "" , "pre_num" , pre_num );
get函数中的第一个参数和第二个参数联合起来组成路径。
第一个参数也必须是一个uvm_component实例的指针,
第二个参数是相对此实例的路径。 一般的, 如果第一个参数被设置为this, 那么第二个参数可以是一个空的字符串。
第三个参数就是set函数中的第三个参数, 这两个参数必须严格匹配,
第四个参数则是要设置的变量
第一个参数详解
当第一个参数为 null 时, UVM会自动把第一个参数替换为uvm_root::get() , 即uvm_top。 换句话说, 以下两种写法是完全等价的
1
2
3
4
5
6
initial begin
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv" , "vif" , input_if );
end
initial begin
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( uvm_root :: get (), "uvm_test_top.env.i_ag t. drv" , "vif" , input_if );
end
既然set函数的第一个和第二个参数联合起来组成路径, 那么在某个测试用例的build_phase中可以通过如下的方式设置
1
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this . env , "i_agt.drv" , "pre_num_max" , 100 );
把this替换为了this.env, 第二个参数是my_driver相对于env的路径
1
2
3
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: get ( this . parent , "drv" , "pre_num_max" , pre_num_max );
或者:
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: get ( null , "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num_max" , p re_num_max );
这些写法都是可以的, set 和 get 的写法没有任何优势。
省略get 语句
set与get函数一般都是成对出现, 但是在某些情况下, 是可以只有set而没有get语句, 即省略get语句
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.3 / my_driver . sv
int pre_num ;
`uvm_component_utils_begin ( my_driver )
`uvm_field_int ( pre_num , UVM_ALL_ON )
`uvm_component_utils_end
function new ( string name = "my_driver" , uvm_component parent = null );
super . new ( name , parent );
pre_num = 3 ;
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
`uvm_info ( "my_driver" , $sformatf ( "before super.build_phase, the pre_num is %0d" , pre_num ), UVM_LOW );
super . build_phase ( phase );
`uvm_info ( "my_driver" , $sformatf ( "after super.build_phase, the pre_num is %0d" , pre_num ), UVM_LOW );
if ( ! uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: get ( this , "" , "vif" , vif ))
`uvm_fatal ( "my_driver" , "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!" );
endfunction
只要使用uvm_field_int注册, 并且在build_phase中调用super.build_phase( ) , 就可以省略在build_phase中的如下get语句
1
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: get ( this , "" , "pre_num" , pre_num );
这里的关键是build_phase中的 super.build_phase 语句, 当执行到driver的super.build_phase时, 会自动执行get语句。 这种做法的前提是:
跨层次的多重设置
如果有多处set 那么, 以层次最高的set 为准, 如果在最高的层次里有多个 set, 则以最后的set 为准, UVM规定层次越高, 那么它的优先级越高
层次不同时
在 uvm_test_top 中设置了 pre_num
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.4 / normal / my_case0 . sv
function void my_case0 :: build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
…
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this ,
"env.i_agt.drv" ,
"pre_num" ,
999 );
`uvm_info ( "my_case0" , "in my_case0, env.i_agt.drv.pre_num is set to 999" , UVM_LOW )
...
endfunction
在 env 中设置 pre_num
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.4 / normal / my_env . sv
virtual function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
…
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 100 );
`uvm_info ( "my_env" , "in my_env, env.i_agt.drv.pre_num is set to 100" , UVM_LOW )
endfunction
则 driver 中获得的 pre_num 是 999, 因为 uvm_test_top 的层次比 env 高
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.4 / normal / my_env . sv
virtual function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
…
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( uvm_root :: get (), "i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 100 );
`uvm_info ( "my_env" , "in my_env, env.i_agt.drv.pre_num is set to 100" , UVM_LOW )
endfunction
则结果为 100, 因为在 env 中的设置, 其层次已经是 uvm_top, 在UVM 树中有最高的层次, 即最高优先级
层次相同时
在 uvm_test_top 中设置 pre_num
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.4 / abnormal / my_case0 . sv
function void my_case0 :: build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
…
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( uvm_root :: get (), "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 999 );
`uvm_info ( "my_case0" , "in my_case0, env.i_agt.drv.pre_num is set to 999" , UVM_LOW )
endfunction
在 env 中设置 pre_num
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.4 / normal / my_env . sv
virtual function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
…
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( uvm_root :: get (), "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 100 );
`uvm_info ( "my_env" , "in my_env, env.i_agt.drv.pre_num is set to 100" , UVM_LOW )
endfunction
这种情况由于发信人都是 uvm_root::get() 所以最后设置的有效, 由于uvm_test_top 的层次比env 的高, 所以会先执行, 而后执行的 env 会覆盖掉先执行的结果,
无论如何, 在调用set函数时其第一个参数应该尽量使用this。 在无法得到this指针的情况下( 如在top_tb中) , 使用null 或者uvm_root::get()
同一层次的多重设置
假设 pre_num在99%的测试用例中的值都是7, 只有在1%的测试用例中才会是其他值, 比较优雅的做法是在 base_test 的build_phase中使用config_db::set
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
classs base_test extends uvm_test ;
function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "env.i_agt.drv" , pre_num_max , 7 );
endfunction
endclass
class case1 extends base_test ;
function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
endfunction
endclass
…
class case99 extends base_test ;
function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
endfunction
endclass
当需要设置为别的值时则
1
2
3
4
5
6
class case100 extends base_test ;
function void build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "env.i_agt.drv" , pre_num_max , 100 );
endfunction
endclass
case100的build_phase相当于如下所示连续设置了两次
1
2
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 7 );
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 100 );
按照时间优先的原则, 后面config_db::set的值将最终被driver得到。
非直线的设置与获取
非直线设置
在 scb 中设置
1
2
3
4
5
6
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.6 / set / my_scoreboard . sv
function void my_scoreboard :: build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
…
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this . m_parent , "i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 200 );
`uvm_info ( "my_scoreboard" , "in my_scoreboard, uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv.pre_num is set to 200" , UVM_LOW );
endfunction
或者
1
2
3
4
function void my_scoreboard :: build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( uvm_root :: get (), "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , 200 );
endfunction
无论哪种方式, 都带来了一个新的问题。 在UVM树中, build_phase是自上而下执行的, scb与i_agt处于同一级别中,
非直线获取
假如要在reference model中获取driver的pre_num的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.6 / get / my_model . sv
function void my_model :: build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
port = new ( "port" , this );
ap = new ( "ap" , this );
`uvm_info ( "my_model" , $sformatf ( "before get, the pre_num is %0d" , drv_pre_num ), UVM_LOW )
void '( uvm_config_db #( int ) :: get ( this . m_parent , "i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , drv_pre_num ));
`uvm_info ( "my_model" , $sformatf ( "after get, the pre_num is %0d" , drv_pre_num ), UVM_LOW )
endfunction
或者
1
void '( uvm_config_db #( int ) :: get ( uvm_root :: get (), "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv" , "pre_num" , drv_pre_num ));
非直线的获取可以在某些情况下避免config_db::set的冗余。 上面的例子在reference model中获取driver的pre_num的值, 如果
config_db机制对通配符的支持
使用完整路径设置
1
2
3
4
5
initial begin
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv" , "vif" , input_if );
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.mon" , "vif" , input_if );
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "uvm_test_top.env.o_agt.mon" , "vif" , output_if );
end
使用通配符
1
2
3
4
5
initial begin
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt*" , "vif" , input_if );
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "uvm_test_top.env.o_agt*" , "vif" , output_if );
`uvm_info ( "top_tb" , "use wildchar in top_tb's config_db::set!" , UVM_LOW )
end
进一步简化
1
2
3
4
initial begin
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "*i_agt*" , "vif" , input_if );
uvm_config_db #( virtual my_if ) :: set ( null , "*o_agt*" , "vif" , output_if );
end
check_config_usage
1
2
3
4
5
6
function void my_case0 :: build_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . build_phase ( phase );
uvm_config_db #( uvm_object_wrapper ) :: set ( this , "env.i_agt.sqr.main_phase" , "default_sequence" , case0_sequence :: type_id :: get ());
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "env.i_atg.drv" , "pre_num" , 999 ); // 把 agt 错写成了 atg , 没有地方接收
uvm_config_db #( int ) :: set ( this , "env.mdl" , "rm_value" , 10 );
endfunction
1
2
3
4
5
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.8 / my_case0 . sv
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . connect_phase ( phase );
check_config_usage ();
endfunction
运行仿真的时候会打印如下信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
UVM_INFO @ 0: reporter [RNTST] Running test my_case0...
UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top [CFGNRD] ::: The following resources have at least one write and no reads :::
============================================================================
default_sequence [/^uvm_test_top\.env\.i_agt\.sqr\.main_phase$/] : (class uvm_pkg::uvm_object_wrapper) ?
-
--------
uvm_test_top reads: 0 @ 0 writes: 1 @ 0
============================================================================
============================================================================
pre_num [/^uvm_test_top\.env\.i_atg\.drv$/] : (int) 999
-
--------
uvm_test_top reads: 0 @ 0 writes: 1 @ 0
============================================================================
上
set_config与get_config => UVM1.2 及以后的版本中已移除
set_config_int == uvm_config_db#(int)::set
get_config_int == uvm_config_db#(int)::get
set_config_string == uvm_config_db#(string)::set
get_config_string == uvm_config_db#(string)::get
set_config_object == uvm_config_db#(object)::set
get_config_object == uvm_config_db#(object)::get
命令行参数来对它们进行设置
config_db比set/get_config强大的地方在于, 它设置的参数类型并不局限于以上三种。 常见的枚举类型、 virtual interface、 bit类 型、 队列等都可以成为config_db设置的数据类型
1
2
< sim command > + uvm_set_config_int =< comp > , < field > , < value >
< sim command > + uvm_set_config_string =< comp > , < field > , < value >
1
< sim command > + uvm_set_config_int = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,pre_num,'h8"
在设置int型参数时, 可以在其前加上如下的前缀: ‘b、 ‘o、 ‘d、 ‘h, 分别表示二进制、 八进制、 十进制和十六进制的数据。 如果不加任何前缀, 则默认为十进制
config_db 的调试
print_config
1
2
3
4
5
文件: src / ch3 / section3 .5 / 3.5.10 / my_case0 . sv
virtual function void connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . connect_phase ( phase );
print_config ( 1 );
endfunction
其中参数1表示递归的查询, 若为0, 则只显示当前component的信息。 print_config的输出结果中有很多的冗余信息。 其运行结果大致如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top [CFGPRT] visible resources:
# <none>
# UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top.env [CFGPRT] visible resources:
# <none>
# UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top.env.agt_mdl_fifo [CFGPRT] visible resources:
# <none>
…
# UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv [CFGPRT] visible resources:
# vif [/^uvm_test_top\.env\.i_agt\.drv$/] : (virtual my_if) X X x x
# -
# pre_num [/^uvm_test_top\.env\.i_agt\.drv$/] : (int) 999
# -
…
#UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.mon [CFGPRT] visible resources:
# vif [/^uvm_test_top\.env\.i_agt\.mon$/] : (virtual my_if) X X x x
# -
…
#UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top.env.mdl [CFGPRT] visible resources:
# rm_value [/^uvm_test_top\.env\.mdl$/] : (int) 10
# -
…
#UVM_INFO @ 0: uvm_test_top.env.o_agt.mon [CFGPRT] visible resources:
# vif [/^uvm_test_top\.env\.o_agt\.mon$/] : (virtual my_if) X X x x
# -
...
它会遍历整个验证平台的所有结点, 找出哪些被设置过的信息对于它们是可见的。
命令行参数UVM_CONFIG_DB_TRACE
1
< sim command > + UVM_CONFIG_DB_TRACE
但是, 无论哪种方式, 如果set函数的第二个参数设置错误, 都不会给出错误信息。
UVM命令行参数汇总
这里的命令行参数指的是运行时的命令行参数, 而不是编译时的命令行参数
打印出所有的命令行参数:
1
< sim command > + UVM_DUMP_CMDLINE_ARGS
指定运行测试用例的名称:
1
2
3
< sim command > + UVM_TESTNAME =< class name >
如:
< sim command > + UVM_TESTNAME = my_case0
在命令行中设置冗余度阈值:
1
2
3
< sim command > + UVM_VERBOSITY =< verbosity >
如 :
< sim command > + UVM_VERBOSITY = UVM_HIGH
设置打印信息的不同行为:
1
2
3
< sim command > + uvm_set_action =< comp > , < id > , < severity > , < action >
如:
< sim command > + uvm_set_action = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,my_driver,UVM_WARNING,UVM_DISPLAY|UVM_COUNT"
重载冗余度:
1
2
3
< sim command > + uvm_set_severity =< comp > , < id > , < current severity > , < new severity >
如 :
< sim command > + uvm_set_severity = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,my_driver,UVM_WAR NING,UVM_ERROR"
设置全局的超时时间:
1
2
3
< sim command > + UVM_TIMEOUT =< timeout > , < overridable >
如:
< sim command > + UVM_TIMEOUT = "300ns, YES"
ERROR到达一定数量退出仿真:
1
2
3
< sim command > + UVM_MAX_QUIT_COUNT =< count > , < overridable >
如 :
< sim command > + UVM_MAX_QUIT_COUNT = 6 , NO
打开phase的调试功能:
1
< sim command > + UVM_PHASE_TRACE
打开objection的调试功能:
1
< sim command > + UVM_OBJECTION_TRACE
打开config_db的调试功能:
1
< sim command > + UVM_CONFIG_DB_TRACE
打开resource_db的调试功能:
1
< sim command > + UVM_RESOURCE_DB_TRACE
使用factory机制重载某个实例:
1
2
3
< sim command > + uvm_set_inst_override =< req_type > , < override_type > , < full_inst_pa th >
如:
< sim command > + uvm_set_inst_override = "my_monitor,new_monitor,uvm_test_top.en v.o_agt.mon"
类型重载:
1
2
3
< sim command > + uvm_set_type_override =< req_type > , < override_type > [, < replace > ]
如:
< sim command > + uvm_set_type_override = "my_monitor,new_monitor"
第三个参数只能为0或者1, 默认情况下为1。
在命令行中使用set_config:
1
2
3
4
< sim command > + uvm_set_config_int =< comp > , < field > , < value >
< sim command > + uvm_set_config_string =< comp > , < field > , < value >
如:
< sim command > + uvm_set_config_int = "uvm_test_top.env.i_agt.drv,pre_num,'h8"
UVM常用宏汇总
宏的定义方式
它有两种定义方式:
一是直接在源文件中中使用define进行定义:
1
2
3
`define MACRO
或者:
`define MACRO 100
二是在编译时的命令行中使用如下的方式:
1
2
3
< compile command > + define + MACRO
或者:
< compile command > + define + MACRO = 100
扩展寄存器模型中的数据位宽:
1
`define UVM_REG_DATA_WIDTH 128
扩展寄存器模型中的地址位宽:
1
`define UVM_REG_ADDR_WIDTH 64
自定义字选择( byteenable) 位宽:
1
`define UVM_REG_BYTENABLE_WIDTH 8
去除OVM中过时的用法, 使用纯净的UVM环境:
1
`define UVM_NO_DEPRECATED
其他
除了上述通用的宏外, 针对不同的仿真工具需要定义不同的宏: QUESTA、 VCS、 INCA分别对应Mentor、 Synopsys和Cadence 公司的仿真工具。 UVM的源代码分为两部分, 一部分是SystemVerilog代码, 另外一部分是C/C++。 这两部分代码在各自编译时需要分别定义各自的宏。
seq_item_port and seq_item_export
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
function void my_agent :: connect_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
super . connect_phase ( phase );
if ( is_active == UVM_ACTIVE ) begin
// seq_item_port 是 uvm_driver 中的成员变量, seq_item_export 是uvm_sequencer 中的成员变量
// 两者通过connect 建立联系后 driver 中就可以通过 get_next_item 任务向sequencer 申请transaction 了
drv . seq_item_port . connect ( sqr . seq_item_export );
end
ap = mon . ap ;
endfunction
task my_driver :: main_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
`uvm_info ( "my_driver" , "main_phase is call" , UVM_LOW )
fork
while ( 1 ) begin
seq_item_port . get_next_item ( req ); // 请求sequence 发送driver
drive_motor ( req );
seq_item_port . item_done ();
end
join
endtask
req
只要类在定义时 extends 某个类的时候传入 uvm_sequence_item 类型的参数req 来代替这个传入的 uvm_sequence_item 类型
Demo1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class motor_driver extends uvm_driver #( motor_transaction );
...
task motor_driver :: main_phase ( uvm_phase phase );
`uvm_info ( "motor_driver" , "main_phase is call" , UVM_LOW )
fork
while ( 1 ) begin
seq_item_port . get_next_item ( req ); // seq_item_port 是 uvm_driver 中的成员变量 已经在agent 中连接到sequencer
drive_motor ( req ); // req 是 motor_driver 定义时传入的类型 motor_transaction
seq_item_port . item_done ();
end
join
endtask
Demo2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
class case1_sequence extends uvm_sequence #( cfg_item );
...
virtual task body ();
`uvm_info ( "case1_sequence" , "case1_sequence is called" , UVM_LOW );
if ( starting_phase != null )
starting_phase . raise_objection ( this );
# 2000 _000 ;
`uvm_info ( "case1_sequence" , "uvm do " , UVM_LOW );
`uvm_do_with ( req , { req . addr == 0 ;})
if ( starting_phase != null )
starting_phase . drop_objection ( this );
endtask
`uvm_object_utils ( case1_sequence )
endclass